Beech KA100 Uncontained TPE331-6 Failure – Inappropriate Repair Scheme (N6756P)
On 16 July 2014 Beechcraft King Air 100 N6756P suffered an uncontained failure of its no 1 Honeywell TPE331-6 turboshaft engine near Bakersfield, California during a private flight. The US National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) explain in their safety investigation report (issued 22 September 2020, 74 months later) that the aircraft…
…was cruising at flight level 190 (19,000 feet amsl), about 30 miles ENE of Bakersfield, when the left engine spooled back. The pilot executed the engine failure in-flight procedures and landed uneventfully at Meadows Field Airport.
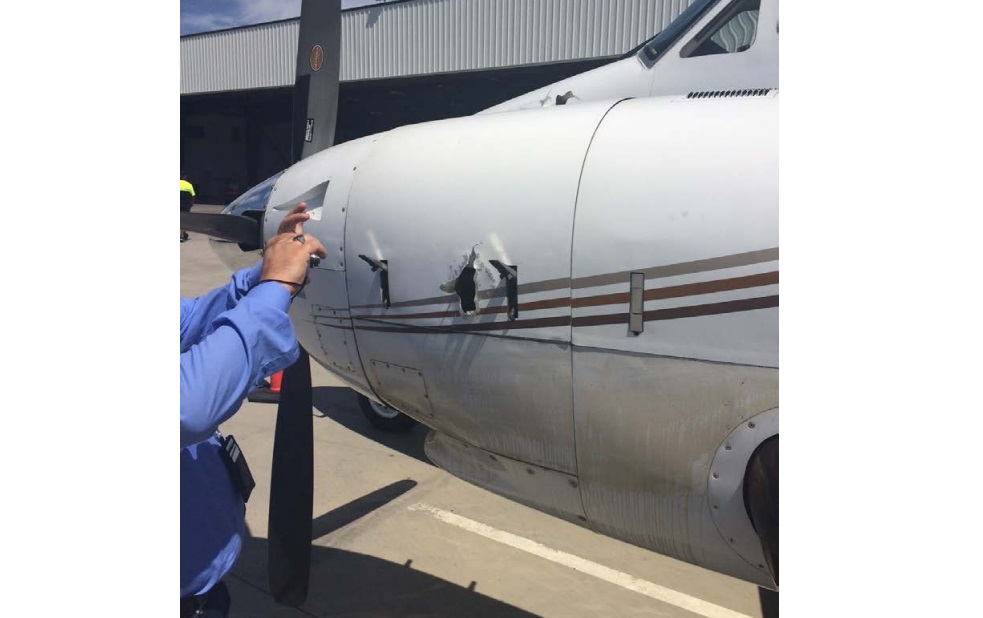
Post flight inspection revealed damage, consistent with an uncontained engine event, to the left nacelle and external damage to the left engine.
Engine Examination and Failure Mode
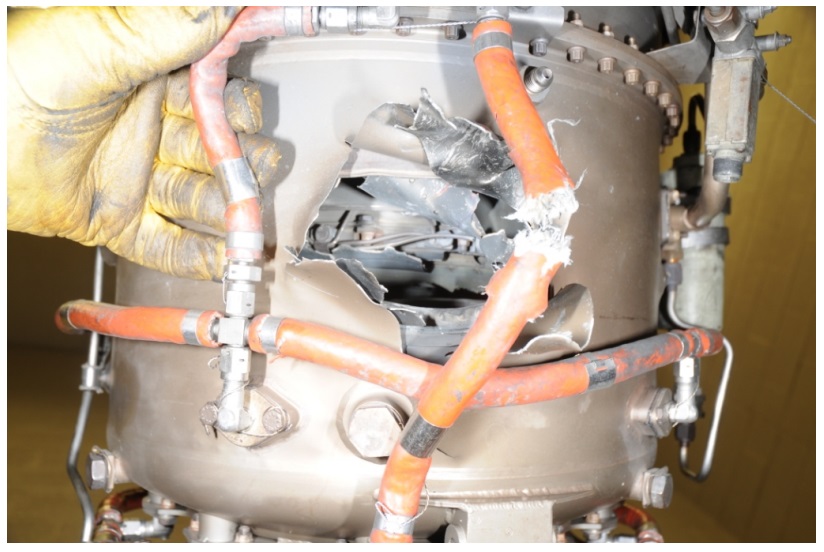
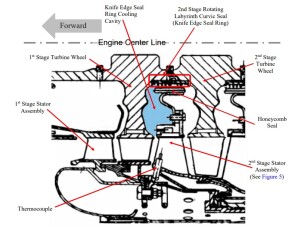
…examination of the left engine revealed an overload failure of the 2nd-stage turbine wheel.
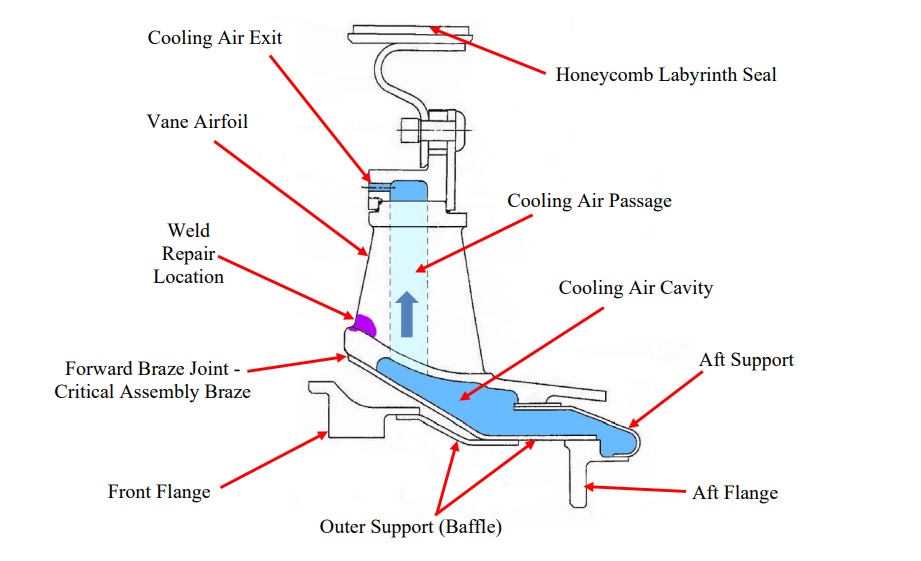
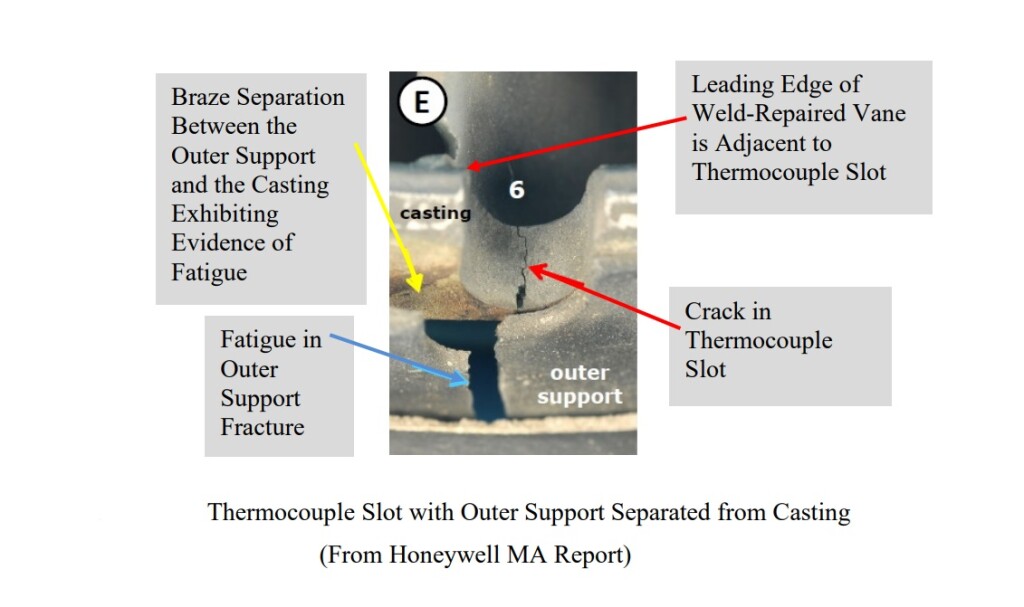
The investigation determined that a repair to a brazed joint on the 2nd-stage main nozzle casting support baffle and outer flange had failed.
Once the seal ring fractured, it sprang open slightly from normal internal stresses, became loose in the cavity, and then migrated axially aft until it contacted the rotating 2nd-stage turbine wheel web and started to machine the web material, weakening it until the overload failure occurred.
According to the engine manufacturer, without the cooling air, metal temperatures of the knife-edge seal ring at the forward and aft ends were estimated to be 1446°F and 1263°F, respectively. Intergranular fractures were initiated after exposure to these high temperatures. The nominal cavity temperature should be 1060°F.
Maintenance History and Repair Approval
The 2nd stage stator assembly forward braze joint was repaired by Texoma Turbines, in Durant, Oklahoma in February 2009. Honeywell do not consider the part repairable. However, a Repair Process Specification (RPS) had been developed independently.
NTSB also noted that:
The original technical documents used to substantiate the repair processes in the RPS could not be located, therefore a review of it could not be done. An FAA technical staff member interviewed from the Fort Worth ACO Branch, believed that there was no technical substantiation data written for this repair and that only the process steps were written by the original DER [Designated Engineering Representative] because the technical substantiation data was not included in the DER’s approval.
It is not known if the DER considered (1) the braze joint oxidation and porosity sensitivity to welding and heat-treatment heat or (2) of the impact of loss of cooling air of this part on any adjacent or downstream components of the engine.
The technical substantiation data should have been retained by the original DER and the original Repair Station; however, he was no longer a DER and not in the DER directory. Guidance for the retention of technical substantiation documents is defined in FAA Order 1350.15C, Records Management, Chapter 11, Flight Safety, Item 8113 Designated Engineering Representative states that original document destruction is not authorized. There is no guidance for the transfer of documents when a DER quits or dies.
NTSB Probable Cause
The failure of the 2nd-stage turbine wheel due to an improper repair of the 2nd-stage stator assembly, which the manufacturer does not consider a repairable item. Contributing to the incident was the designated engineering representative’s approval of the repair process.
Safety Resources
Also see these Aerossurance articles:
- NDI Process Failures Preceded B777 PW4077 Engine FBO
- Japanese Jetstar Boeing 787 GEnx-1B Engine Biocide Serious Incident
- CFM56-7 HPC Titanium Fire Due to VSV Maintenance Assembly Error (United Boeing 737-924)
- Uncontained CF6-80 Failure: American B767-300 28 Oct 2016
- USAF Engine Shop in “Disarray” with a “Method of the Madness”: F-16CM Engine Fire
- Inadequate Maintenance, An Engine Failure and Mishandling: Crash of a USAF WC-130H
- Engine Failure after Inadvertently Being Put Back into Service Incomplete
- NTSB Confirms United Airlines Maintenance Error After 12 Years
- Fire After O-Ring Nipped on Installation
- 17 Year Old FOD and a TA-4K Ejection
- Machining Defect Cause of V2500 Failure
- ‘Aggressive’ Grit Blasting Maintenance Leads to Engine Fire & IFSD
- Micro FOD: Cessna 208B Grand Caravan Engine Failure & Forced Landing
- Cessna 208 Forced Landing: Engine Failure Due To Re-Assembly Error
- B767 Fire and Uncommanded Evacuation After Lockwire Omitted
- UPDATE 10 July 2021: Forced Landing after CAMO Underestimated Operation in Dusty Environments
- UPDATE 13 November 2021: Bell 407 Rolls-Royce 250-C47B Uncontained Engine Failure after Bearing Failure



Recent Comments